Enabling compliance while preserving privacy: Panther’s compliance integrations explained

Table of Contents:
The Web3 ecosystem almost unanimously agrees on the benefit of users preserving their privacy while retaining permissionless access to distributed ledger technology.
This shared understanding, however, tends to face an equally strong pushback (particularly from regulatory authorities) when we are reminded that privacy, without checks and balances, can become a shield for illicit activities. Indeed, the purpose of blockchain technology and cryptocurrency is not to enable criminal actors to surpass Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF) regulations or to find a way around sanctions. Rather, permissionless tools are preferred by the Web3 ecosystem based on its initial ideology, centered on the pursuit of individual freedoms and the attempt to decentralize currency and eliminate intermediaries on the Web.
For most people, privacy and compliance seem to be at odds. However, the latest technological advances, such as zero-knowledge proofs, are paving the way for innovation. Combining these technologies with an approach based on ZK disclosures and decentralizing access to compliance, Panther is pioneering privacy-preserving access to DeFi while enabling new compliance mechanisms.
Here's how.
Understanding risks and challenges
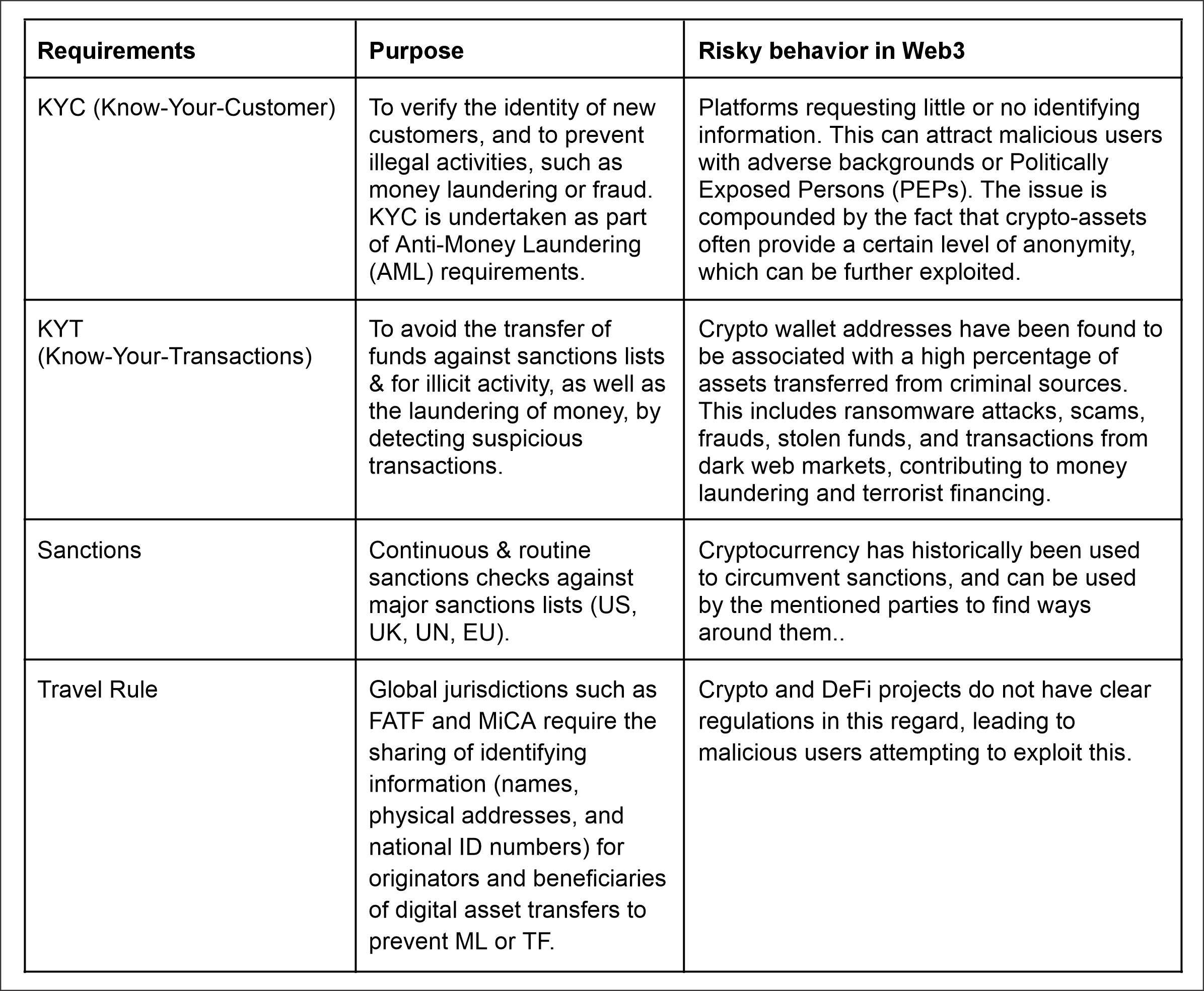
To avoid a scenario where a malicious actor can exploit the protocol to commit crimes, it's important to first understand the different regulations, their purpose, and the risks a privacy-preserving solution needs to address.
Some of the most important regulations are:
Conceptualizing a solution
Considering the difficulties in developing a decentralized solution that preserves privacy and enables compliance, Panther designed an approach that utilizes three essential components. These elements collectively form a pathway to achieve compliance by leveraging the protocol's zero-knowledge characteristics.
Panther's solution is based on:
Third-party compliance vendor integrations
Panther has built a system that retains neutrality by integrating compliance providers that accept multiple types of verification. These systems are called "multi-compliance vendors" as they allow users to choose from various compliance providers while retaining a decentralized approach.

The Panther DAO has been commissioned to select a multi-compliance vendor that aligns with its interests, a discussion taking place in Panther's forum. When integrating these providers, the following requirements are taken into consideration:
- Ability to blacklist PEPs or newly flagged individuals based on unverified identities.
- Blacklists for verified EoAs.
- Ability to perform checks to create an "allowlist" that works on- and off-chain.
- Preferably, maintaining an on-chain verification list through oracles/smart contracts.
- Performing validations at deposit and withdrawal.
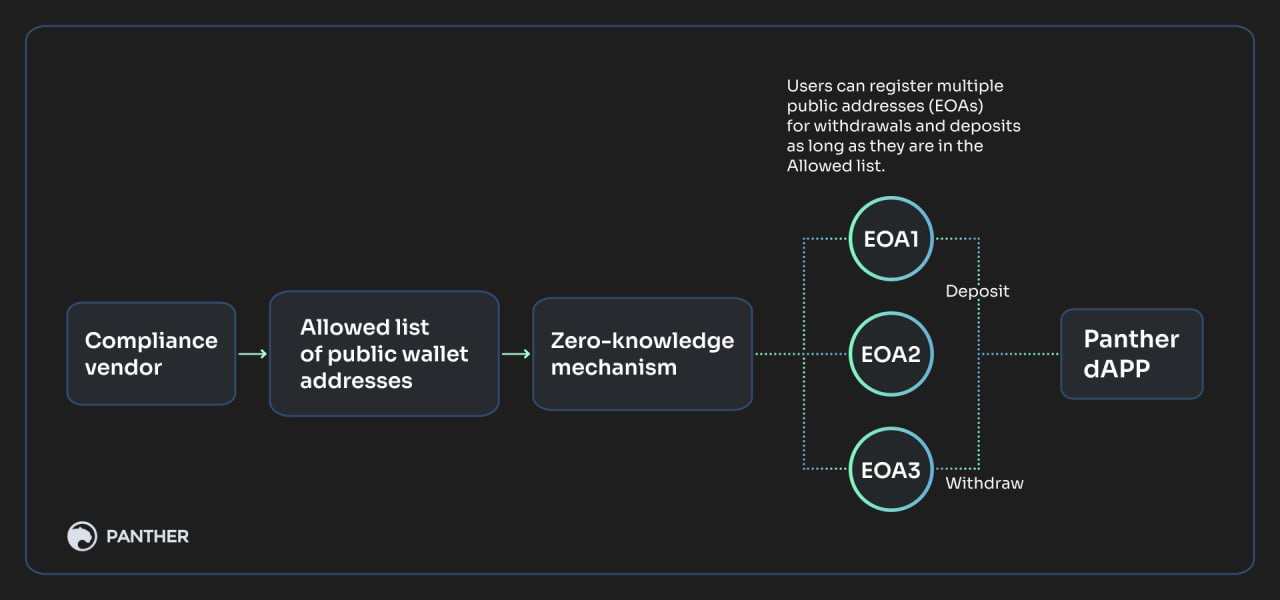
- Optionally, allowing users to register multiple addresses. This is suggested so that users can break the on-chain link between their transactions by withdrawing and depositing from different addresses.
- Optionally, using a zero-knowledge proof to allow users to create new accounts once they have passed verification.
Within Panther's solution, compliance providers need to be able to process users' data without the protocol learning it, proving a user's ownership of their wallet and giving them a zero-knowledge proof that attests to the validity of their statements. This allows users to access Panther but maintains the protocol's neutrality. The diagram below exemplifies this process:
zAccounts

Within Panther, users are identified through their zAccount, a concept similar to a bank account in that it englobes all of a user's transactions within a single reference point. zAccounts attest to users' compliance verification while retaining zero-knowledge properties. In other words, they prove that a user has passed verification (and the type of verification passed), but they do not store any private information about users.
As you saw in the diagram above, Panther is interested in allowing users to have multiple accounts for withdrawals and depositing, all of which would be connected to their zAccount. This would prevent users from creating obvious, observable on-chain links between their public wallets and zAccounts.
Zones
Although they primarily serve a different purpose (which will be covered in an upcoming article), Zones also play a part in the design of Panther's compliance integrations.
This is because Panther's overall compliance solution covers multiple Zones. Zones are logical partitions of liquidity within Shielded Pools, each managed by a different ZM (Zone Manager). ZMs can determine what compliance information their Zones require from users and control the integration of specific compliance vendors into their Zones to fit their particular goals.
The requirements ZMs set for users, the types of verifications these users undergo, and other factors related to Zones also influence users' transaction limits, the types of movements they're allowed to do, and other variables. As such, Zones are also vital in Panther's design to enable compliance.
Conclusion
With a first-of-its-kind approach to zero-knowledge DeFi access with enabled compliance, Panther attempts to create a new approach to DeFi for institutions and retail users alike. The protocol's unique architecture offers a comprehensive solution for regulated entities to function in the DeFi space while remaining neutral at a protocol level.
Panther has also given much thought to flexibility, enhancing the possibilities for users and Zone Managers. The protocol is committed to aligning the needs of users, regulators, and institutions in the DeFi space. Its vision puts users in control of who views their data while remaining able to comply with regulations, two characteristics previously never combined in the DeFi space.
About Panther
Panther is a cross-protocol layer that uses zero-knowledge technology to build DeFi solutions that meet regulatory requirements and satisfy users' on-chain data privacy needs. The goal of Panther is to allow seamless access to DeFi and create a cross-chain-supported architecture that serves different use cases. Panther's zero-knowledge primitives are also generalizable to KYC, selective disclosures between trusted parties, private ID, voting, and data verification services.
Website · One-pager · Lite Paper · Twitter · Telegram · Discord
